Securing RAG & Agentic Chatbots with OWASP LLM Top 10
Over the past two years, I’ve been working on AI applications 🤖, guiding organizations to build AI governance frameworks, responsible AI policies, and deploying production-ready systems.
From this experience, I can confidently say: figuring out the technical part is fun 🎉 and often the easier part. The bigger challenge—and where most time is spent—is building responsible AI practices and governance frameworks that scale across the enterprise.
In my previous post, I discussed how to approach AI governance and frameworks at the enterprise level. In this post, let’s go through a quick 101 on designing AI application architectures responsibly.
📖 Reference: OWASP Top 10 for LLM Applications
🏗️ Why Architecture Matters in AI Applications
The AI landscape changes daily ⚡, making it difficult to lock down a future-proof architecture. A good starting point is defining:
- 🎯 The objective of the AI application
- 🖥️ The platform on which it will be built
These early decisions shape the system design and architecture.
For this discussion, let’s use an example: a domain-specific chatbot 💬 that uses customer data and a foundational model to generate responses. To make it more complex, we’ll add tool calling 🛠️ and agents 🕹️ for real-time, domain-specific functions.
🗂️ Base Architecture
Figure 1 – Basic Chatbot Architecture
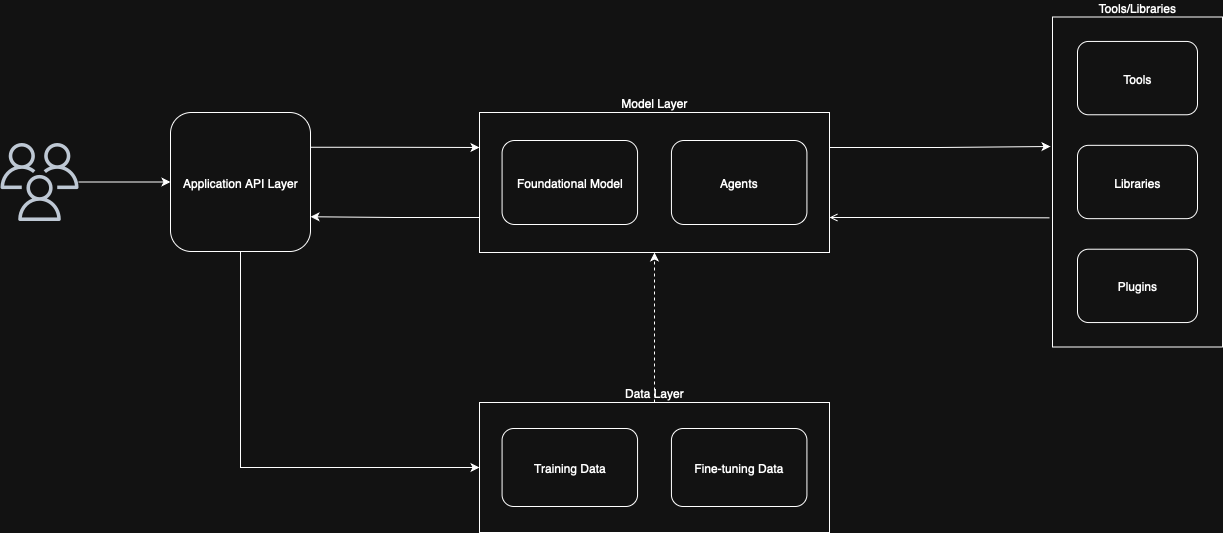
At first glance 👀, this architecture may look ready for production. However, during an architecture review board 🧑💻 or discussions with security and compliance teams 🔐, this base setup will quickly fall short.
Why? Because we haven’t yet considered the security, safety, and compliance risks 🚨 that can be exploited in such a design.
Just as we use OWASP Top 10 to secure web applications 🌐, OWASP has released the LLM Top 10—a framework to secure AI and LLM-powered applications.
🌍 OWASP GenAI Security Project
The OWASP GenAI Security Project is a global, open-source initiative dedicated to identifying, mitigating, and documenting security and safety risks associated with generative AI technologies, including large language models (LLMs), agentic AI systems, and AI-driven applications.
✅ This framework is an excellent starting point for both beginners 🚀 and experts 🧠 to evaluate architecture, identify vulnerabilities, and mitigate risks.
❓ Key Security Questions for Chatbot Applications
When designing AI applications, consider:
- 🛡️ How will the application handle prompt injection (at both input and output)?
- 🔐 How is sensitive data (PII) handled? Is it anonymized or masked?
- 📦 How is training data stored and secured? What if training data is poisoned?
- 🧩 How are custom libraries and tools secured? Are they scanned for vulnerabilities?
- 📢 Does the application disclose its use of AI and align with Responsible AI policies?
- 🧬 How are fine-tuned or custom models protected? What happens if they’re exposed?
🔟 OWASP LLM Top 10
Here are the 10 key risks to consider:
- 📝 LLM01: Prompt Injection
- ⚠️ LLM02: Insecure Output Handling
- 🧪 LLM03: Training Data Poisoning
- 🛑 LLM04: Model Denial of Service
- 🔗 LLM05: Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
- 🔒 LLM06: Sensitive Information Disclosure
- 🧩 LLM07: Insecure Plugin Design
- 🤖 LLM08: Excessive Agency
- 👤 LLM09: Overreliance
- 🕵️ LLM10: Model Theft
🗺️ Mapping to Architecture
Figure 2 – Mapping OWASP LLM Top 10 to Architecture
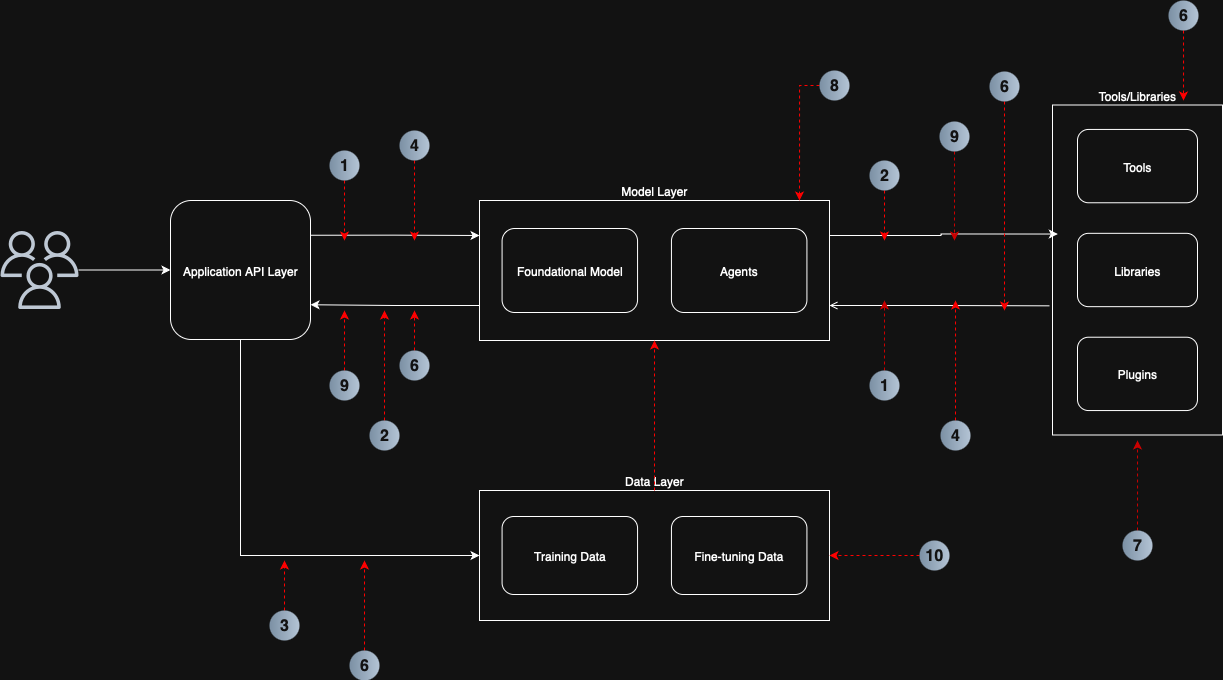
By applying these guidelines, you can create a matrix 📊 that scores your architecture against the OWASP framework. This provides:
- A baseline security posture 🔐 for AI applications
- A reference template 📑 for future system design
- A governance-aligned approach 🏛️ to AI architecture
📊 OWASP LLM Top 10 – Scoring Matrix Template
Each item can be scored on a scale of 1–5 (1 = poor 🚫, 5 = strong 💪).
| 🆔 OWASP Risk ID | 🛑 Risk Category | 📖 Description | 🏷️ Score (1-5) | 🛠️ Notes / Mitigation Plan |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLM01 | Prompt Injection | Protection against prompt injection attempts | ||
| LLM02 | Insecure Output Handling | Validation and sanitization of model outputs | ||
| LLM03 | Training Data Poisoning | Safeguards against corrupted training data | ||
| LLM04 | Model Denial of Service | Rate limiting, monitoring, and throttling | ||
| LLM05 | Supply Chain Vulnerabilities | Verification of datasets, plugins, libraries | ||
| LLM06 | Sensitive Info Disclosure | Anonymization, masking, encryption of PII | ||
| LLM07 | Insecure Plugin Design | Plugin isolation and secure coding practices | ||
| LLM08 | Excessive Agency | Controls to limit agent autonomy | ||
| LLM09 | Overreliance | Human-in-the-loop and fallback mechanisms | ||
| LLM10 | Model Theft | Access controls, encryption, monitoring |
🧪 Sample Scoring Matrix: Chatbot + RAG + Agent
Here’s a worked example for a domain-specific chatbot 💬 that uses RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation 📚) with tool calling 🛠️ and agentic workflows 🤖.
| 🆔 OWASP Risk ID | 🛑 Risk Category | 📖 Description | 🏷️ Score (1-5) | 🛠️ Notes / Mitigation Plan |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLM01 | Prompt Injection | Moderate risk, mitigated with input/output filters | 3 | Add context validation + regex sanitization |
| LLM02 | Insecure Output Handling | High risk due to tool execution | 2 | Enforce strict schema validation + guardrails |
| LLM03 | Training Data Poisoning | Moderate risk if knowledge base ingestion is not validated | 3 | Add data quality checks + signed data sources |
| LLM04 | Model Denial of Service | High risk (agents can loop or generate heavy queries) | 2 | Add rate limiting + monitoring |
| LLM05 | Supply Chain Vulnerabilities | Plugins & APIs could be compromised | 3 | Use dependency scanning & signed artifacts |
| LLM06 | Sensitive Info Disclosure | RAG may retrieve PII or confidential data | 2 | Add anonymization + retrieval filters |
| LLM07 | Insecure Plugin Design | High risk with tool calling | 2 | Implement zero-trust plugin execution |
| LLM08 | Excessive Agency | Agents may overstep bounds | 2 | Add role-based execution policies |
| LLM09 | Overreliance | Users may blindly trust answers | 3 | Add disclaimers + confidence scoring |
| LLM10 | Model Theft | Lower risk in managed cloud (e.g. Bedrock) | 4 | Rely on provider safeguards + IAM |
🎯 Final Thoughts
The OWASP LLM Top 10 is not just a checklist—it’s a security lens 🔍 for AI system design.
By using it in combination with your enterprise AI governance framework, you’ll be better equipped to build secure 🔐, responsible 🌱, and accountable 📊 AI applications that can withstand real-world risks.
